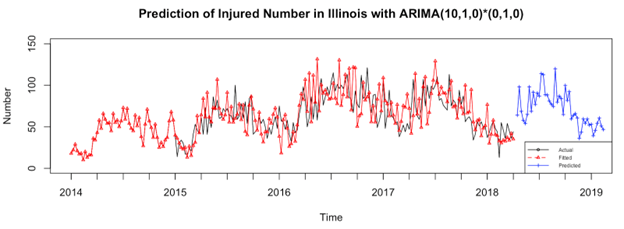
Word Cloud
66% of incidents had a completed "notes" field, on which we conducted text analysis. Words deemed too "generic" were removed. Some noteworthy observations:
- "Man" appears far more frequently than "Woman"
- "Home" is the most common location term"
- "Drug is the most common term
- "Car" and "Drive" both occur quite frequently
- "Stolen", "Robbery", and "Gang" - common terms associated with criminal activity
- "Self" appears a notable amount of times
- "Shot", "Gun", "Fire", "Found", "Suspect", "Victim", "Shoot", "Near", "Inj", "Vic", "During", "Perp", "Unclear", "Report", "Stop", "Co", "Cal", "Up", "One", "Time", "Two", "Recov", "Poss", "Attempt", "Approx", "Street", "Apart", "St", "Hi", "Weapon", "Di", "Another", "Between", "Over"